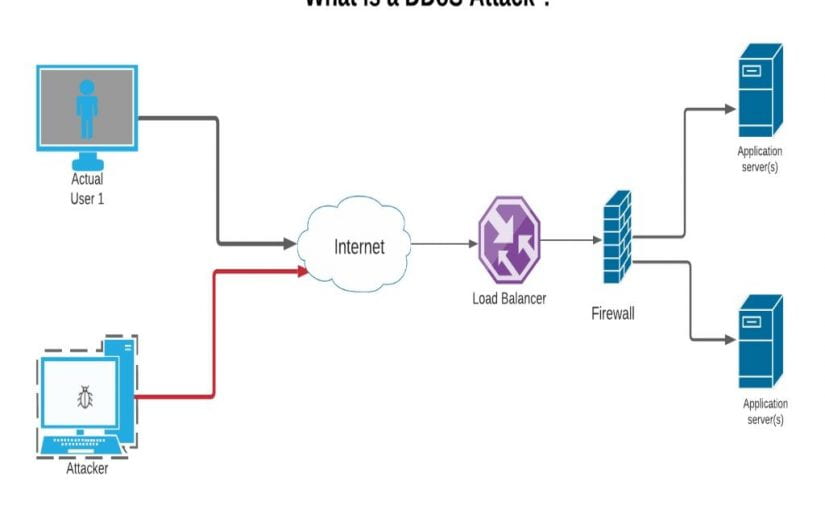
Were you aware that a DDoS attack could bring down your website in a couple of minutes? Hackers focus on your website and load your server and network. Your website is unavailable and cannot be completely offline. It’s not available. We’re going to show you how to prevent DDoS attacks.
DDoS Attacks Definition:
DDoS is a cyber-targeted attack on a website or device that sends out a flood of traffic from a malicious attacker, either from single sources or from multiple. The primary objective of DDoS is to make a machine or network resource unavailable by disrupting the services of a host connected to the Internet temporarily or to its real user. If we do not use adequate security practises and tools, your application becomes non-functional.
The malicious attacker uses several affected computer systems or devices or IoT devices. The DDoS attacks are all more effective with compromise devices.
Types of DDoS Attacks:
- Volume Based Attacks
- Protocol Attacks
- Application Layer Attacks
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks:
- Traffic Monitoring
- Define a DDoS Attack Plan
- Activate WAF
- Rate Limit
- Passive Cache
- Cloud Based DDoS Mitigation
You can read more in detail about DDoS attacks and how to mitigate them here